语法:
变量
- 动态类型 弱类型 大小写敏感 默认全局 带GC
- 类型:nil、boolean、number、string、function、userdata(用户自定义类型)、tread、table
语句
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56-- 赋值 --
a,b = "hello", 15
print("a = ", a)
print("type of a = ", type(a))
print("b = ", b)
print("type of b = ", type(b))
--[[
多行注释 d
]]
-- 交换 --
a,b = b,a
print("a = ", a)
print("b = ", b)
-- 分支 if boolean: false、nil。 0 != false
if b == 15 then
print("b = 15")
elseif b ~= 16 then
print("b != 15")
else
print("b = ", b)
end
-- 循环: 有break 无continue
-- for 起始,终值,增值
for i = 1, 10 ,3 do
print("i = ", i)
end
-- while
d = 1
while d <= 5 do
print(d)
d = d + 1
end
-- repeat until (do while)
ans = 15
repeat
print("guess the password (little than 100)")
a =tonumber(io.read())
if a == ans then
print("You are right!")
break
elseif a > ans then
print(a,"Too big")
else
print(a,"Too small")
end
until false
-- 数学运算 + - * /(//) % ^
-- 加 减 乘 除(取整) 取余 幂
print("5^3 = ", 5^3)
-- 关系运算 > < >= <= == ~=(不等)
-- 逻辑运算 and(&&) or(||) not(!)
数据结构 Table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20-- table
-- 下标从一开始
-- 可以看作为键值对,没有键值,则默认的位置下标为键值(去掉中间存在键值的)
-- table.key or talbe["key"]
a = {1, 2, 3,pos ={"abc", "ddd", ["z"] = "zz"}, x = 123, y = 456, 7}
print(a[6])
print(a["x"])
print(a.y)
print(a.pos.z)
-- 遍历
for k,v in pairs(a) do
if type(k) == table then
for key, val in pairs(k) do
print(key, ":", val)
end
else
print(k, ":", v);
end
end
function 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34-- function
-- 有多个值返回的,从第一个返回的值开始接收,多余的丢弃
add = function(a, b)
return a + b
end
print(add(1,2))
function func(a, b)
return a - b, a * b, 10
end
ans1, ans2 = func(5,2)
print(ans1, ans2)
-- 高阶函数 第一类(first class)
-- 即返回值或参数为函数
function p(f, a, b)
print("a", a)
print("b", b)
print("f(a,b)", f(a,b))
end
p(func, 1, 2)
-- 变参 #v == length(v)
function Sum(...)
local sum = 0
local args = {...}
for k,v in pairs(args) do
sum = sum + v
end
return #args, sum
end
print(Sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9))
运算符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21-- 运算符
-- # 求长度 : 用于普通数组,用于表不准确,存在未定义事件(下标不连续,不是整数等),无法计算长度
a = {1, 2, 3, nil, x = "ss", nil}
print(#a)
-- 连接符 .. 性能消耗大
a = "ab"
b = "cd"
c = a..b
print(c)
-- 逻辑运算符 and or not (与其他语言基本一致)
-- 优先级 and > or
-- 右结合
print(2^3^2) -- <--(2^(3^2))
-- 位运算 & | ~ ~ >> <<
-- 与 或 非 异或 位运算
-- 3 0011
-- 5 0101
print(3~5)
函数库:例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25-- ""有转译, [[]]无转义
a = "a\nb\\c 0b110"
b = [[d \ \ \ \ \ cdca\c\]]
print(a, ",", b)
-- 调用函数
print(string.upper(a))
print(b:upper())
--string 正则匹配与标准不完全一致
--table
a = {1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8}
table.insert(a, 1, 2)
table.remove(a, 2)
table.sort(a)
for k, v in pairs(a) do
print(k, ":", v)
end
print(table.concat(a, "+"))
--math
math.randomseed(os.time())
print(math.random(1,100))
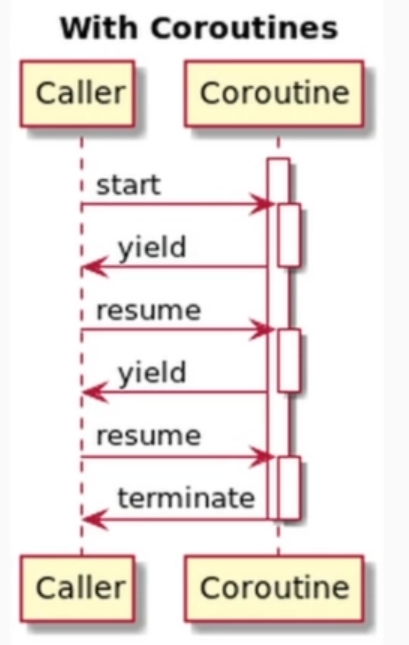
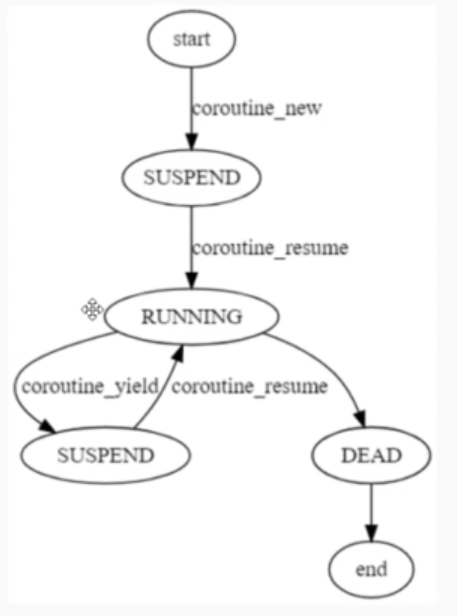
协程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34-- 协程:与Unity协程基本一致,执行到yield,下次执行从yeild后继续
-- thread 线程 协程 进程
--type(co) = thread
co = coroutine.create(
function()
print("coroutine running...")
coroutine.yield()
print("coroutine continue...")
end
)
-- 运行协程
coroutine.resume(co)
coroutine.resume(co)
co = coroutine.create(
function(a,b)
print(a+b)
v1,v2 = coroutine.yield("a", 0)
print("v1 = ", v1, "v2 = ", v2)
end
)
a1,a2,a3 = coroutine.resume(co, 2, 3)
print(a1, a2, a3) -- a1:执行结果(成功/失败) a2,a3(yield返回值)
coroutine.resume(co, 1, 2) -- 第二次调用时传入的参数会作为yeild的返回值
-- type(func) == function
func = coroutine.wrap(
function(i)
print(i)
end
)
OO 面向对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86-- 简易面向对象实现代码
-- 定义对象
local Monster = {
name = "Monster",
HP = 100,
pos = {x = 10, y = 10},
TakeDamage = function(self, damage)
self.HP = self.HP - damage
end
}
local Monster2 = {HP = 200}
--[[
-- 增加方法,传入对象
Monster.TakeDamage = function(self, damage)
self.HP = self.HP - damage
end
function Monster:TakeDamage(damage)
self.HP = self.HP - damamge
end
]]
Monster.TakeDamage(Monster2, 10)
print(Monster.HP)
print(Monster2.HP)
-- Monster.TakeDamage(Monster, 10),即将Monster作为TakeDamage的第一个参数
Monster:TakeDamage(10)
------------------------------------------
-- 定义类
-- 通过原表
CMonster = {
name = "Monster",
HP = 1000,
TakeDamage = function(self, damage)
self.HP = self.HP - damage
end
}
ObjMonster = {pos = {x = 10, y = 10}}
-- 设置原表 -- 该值或加值,调用的是__newindex
setmetatable(
ObjMonster,
{
__index = CMonster,
__newindex = CMonster -- 若__newindex = CMonster 则修改会影响原表
}
)
print(ObjMonster.HP)
ObjMonster.HP = 200
-- 定义new 方法,用于新建对象
CMonster = {
name = "Monster",
HP = 1000,
TakeDamage = function(self, damage)
self.HP = self.HP - damage
end ,
Show = function(self)
print(self.name, ":", self.HP, ":", self.x, ";", self.y)
end
}
-- 设置CMonster的__index, 设置原表时就不需要新建一个表来设置__index了
CMonster.__index = CMonster
function CMonster:new(name, hp, x, y)
local obj = {}
obj.name = name
obj.HP = hp
obj.x = x
obj.y = y
setmetatable(obj, CMonster)
return obj
end
-- 设置CMonster的原表,使其调用可以直接使用 () 来调用new或其他函数
setmetatable(CMonster, {__call = function(self, name, hp, x, y)
return self:new(name, hp, x, y)
end})
obj1 = CMonster("mon", 300, 100, 100)
obj1:Show()
obj1:TakeDamage(250)
obj1:Show()
类的继承的简单实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35-- 继承
-- 引用上一个文件的CMonster类
local Cm = require("t6")
local obj1 = Cm("Monster", 100, 10, 10)
obj1:Show()
-- 定义一个新类
local MMonster = {
MP = 200,
Attack = function(self)
print("Attacking...")
self.MP = self.MP - 10
end
}
-- 定义其原表未Cm,即模拟继承的效果
setmetatable(MMonster, {
__index = Cm,
__call = function(self, name, HP)
local obj = Cm(name, HP)
setmetatable(obj, {__index = MMonster})
return obj
end
})
-- 多态的实现,即在新类中定义原表中存在的方法,模拟多态的实现
function MMonster:Show()
print("M Monster:", self.name, self.HP, self.MP)
end
local mm = MMonster("MMonster1", 100)
mm:Show()
mm:TakeDamage(10)
mm:Show()
简单封装的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36-- 实现Monster类,并进行封装
local Monster = {}
Monster.HP = 100
Monster.x = 1000
Monster.y = 10
Monster.type = "Monster"
function Monster:GetHP()
return self.HP
end
function Monster:TakeDamage(damage)
self.HP = self.HP - damage
end
function Monster:SetHP(hp)
self.HP = hp
end
function Monster:new()
local obj = {HP = Monster.HP, x = Monster.x, y = Monster.y} -- 默认值
setmetatable(obj, Monster)
-- __index 定义新表,表示哪些属性可以被obj访问
Monster.__index = {GetHP = Monster.GetHP, TakeDamage = Monster.TakeDamage, type = Monster.type}
-- __newindex 访问不存在的域时的调用 例如 obj.type = “ddd" 三个分别对应function的三个参数
Monster.__newindex = function(tab, key, value)
if key == "type" then
print("Forbiden orerate.")
return
end
rawset(tab, key, value)
end
return obj
end
return Monster1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12-- 引用并测试
local CMonster = require("t9")
local cm = CMonster:new()
print(cm:GetHP())
cm:TakeDamage(10)
cm.type = "Player" -- Forbiden orerate.
--cm:SetHP(100) -- attempt to call a nil value (method 'SetHP') 无法访问,即设置为私有了
print(cm.z) -- nil
cm.z = 20
print(cm.z) -- 20
闭包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17-- 闭包:通过一系方法,将函数内部的变量(局部变量)转化为全局变量
-- 如下,
function Counter()
i = 0
return function()
i = i + 1
return i
end
end
local cn = Counter()
print(cn())
print(cn())
print(cn())
print(cn())
print(cn())
print(cn())